Which Of The Following Will Most Likely Occur In An Economy If More Money Is Demanded
Chapter 24. The Aggregate Need/Aggregate Supply Model
24.iv Shifts in Aggregate Demand
Learning Objectives
By the end of this section, yous will be able to:
- Explicate how imports influence aggregate demand
- Identify ways in which business concern confidence and consumer confidence can affect aggregate demand
- Explain how authorities policy can change aggregate need
- Evaluate why economists disagree on the topic of tax cuts
As mentioned previously, the components of aggregate demand are consumption spending (C), investment spending (I), government spending (Thousand), and spending on exports (X) minus imports (M). (Read the following Clear It Up feature for explanation of why imports are subtracted from exports and what this ways for aggregate demand.) A shift of the Advert curve to the correct means that at least one of these components increased so that a greater amount of total spending would occur at every price level. A shift of the Advertizement curve to the left ways that at least one of these components decreased so that a bottom amount of full spending would occur at every price level. The Keynesian Perspective will discuss the components of amass demand and the factors that affect them. Hither, the discussion volition sketch two broad categories that could crusade AD curves to shift: changes in the behavior of consumers or firms and changes in regime tax or spending policy.
Practise imports diminish aggregate demand?
We have seen that the formula for aggregate need is AD = C + I + G + Ten – One thousand, where One thousand is the total value of imported goods. Why is there a minus sign in front of imports? Does this hateful that more imports volition result in a lower level of aggregate need?
When an American buys a strange product, for example, information technology gets counted along with all the other consumption. So the income generated does not go to American producers, but rather to producers in another country; it would be wrong to count this as part of domestic demand. Therefore, imports added in consumption are subtracted back out in the K term of the equation.
Because of the way in which the need equation is written, it is piece of cake to make the mistake of thinking that imports are bad for the economy. Merely continue in mind that every negative number in the G term has a corresponding positive number in the C or I or Thousand term, and they always abolish out.
How Changes past Consumers and Firms Can Affect Ad
When consumers experience more confident about the future of the economic system, they tend to consume more. If business organization confidence is high, then firms tend to spend more on investment, believing that the hereafter payoff from that investment will be substantial. Conversely, if consumer or business organisation confidence drops, then consumption and investment spending decline.
The University of Michigan publishes a survey of consumer conviction and constructs an index of consumer conviction each month. The survey results are then reported at http://world wide web.sca.isr.umich.edu, which suspension downwards the change in consumer conviction amongst dissimilar income levels. According to that index, consumer confidence averaged effectually ninety prior to the Great Recession, and so it barbarous to beneath sixty in late 2008, which was the lowest it had been since 1980. Since then, confidence has climbed from a 2011 low of 55.8 dorsum to a level in the low 80s, which is considered close to being considered a healthy state.
1 measure of business confidence is published by the OECD: the "business organization tendency surveys". Concern opinion survey data are collected for 21 countries on future selling prices and employment, amid other elements of the business climate. Subsequently sharply declining during the Cracking Recession, the measure has risen above cipher again and is back to long-term averages (the indicator dips below zero when business outlook is weaker than usual). Of course, either of these survey measures is not very precise. They tin withal, suggest when confidence is rising or falling, as well every bit when information technology is relatively high or low compared to the by.
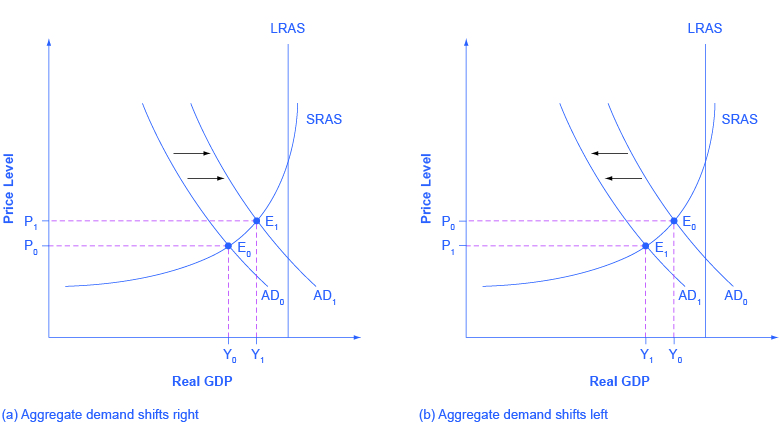
Because a rise in confidence is associated with higher consumption and investment need, it will atomic number 82 to an outward shift in the Advert curve, and a movement of the equilibrium, from E0 to Eastward1, to a college quantity of output and a higher cost level, every bit shown in Figure ane (a).
Consumer and business organisation conviction ofttimes reflect macroeconomic realities; for example, confidence is normally loftier when the economic system is growing briskly and low during a recession. However, economic confidence can sometimes ascension or fall for reasons that exercise not have a close connection to the immediate economy, like a run a risk of war, election results, foreign policy events, or a pessimistic prediction about the future by a prominent public effigy. U.Southward. presidents, for example, must be careful in their public pronouncements about the economy. If they offering economical pessimism, they risk provoking a decline in conviction that reduces consumption and investment and shifts Advertizement to the left, and in a self-fulfilling prophecy, contributes to causing the recession that the president warned confronting in the first place. A shift of Ad to the left, and the corresponding move of the equilibrium, from East0 to E1, to a lower quantity of output and a lower price level, is shown in Figure 1 (b).
How Authorities Macroeconomic Policy Choices Can Shift AD
Government spending is one component of Advertizing. Thus, higher government spending will cause Ad to shift to the right, as in Figure i (a), while lower authorities spending will cause AD to shift to the left, equally in Effigy one (b). For example, in the United states, government spending declined past iii.2% of Gross domestic product during the 1990s, from 21% of Gross domestic product in 1991, and to 17.8% of Gdp in 1998. However, from 2005 to 2009, the summit of the Great Recession, government spending increased from 19% of Gross domestic product to 21.iv% of Gdp. If changes of a few percentage points of GDP seem small to yous, remember that since Gross domestic product was about $14.4 trillion in 2009, a seemingly small modify of two% of Gdp is equal to close to $300 billion.
Tax policy can bear on consumption and investment spending, too. Tax cuts for individuals will tend to increase consumption demand, while tax increases volition tend to diminish information technology. Taxation policy can also pump up investment demand by offering lower tax rates for corporations or tax reductions that benefit specific kinds of investment. Shifting C or I volition shift the Advertisement bend as a whole.
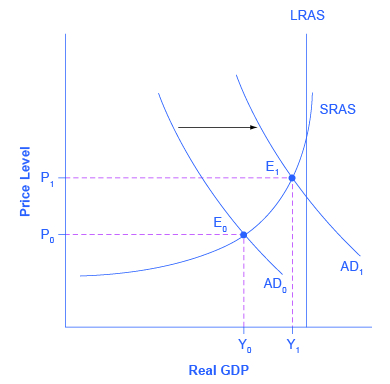
During a recession, when unemployment is high and many businesses are suffering low profits or even losses, the U.Due south. Congress ofttimes passes tax cuts. During the recession of 2001, for instance, a tax cut was enacted into police force. At such times, the political rhetoric often focuses on how people going through hard times need relief from taxes. The aggregate supply and aggregate demand framework, even so, offers a complementary rationale, every bit illustrated in Figure 2. The original equilibrium during a recession is at point Eastward0, relatively far from the total employment level of output. The taxation cut, past increasing consumption, shifts the Advertising curve to the right. At the new equilibrium (E1), existent Gross domestic product rises and unemployment falls and, because in this diagram the economic system has not even so reached its potential or total employment level of GDP, whatsoever rise in the price level remains muted. Read the post-obit Clear It Upward feature to consider the question of whether economists favor tax cuts or oppose them.
Exercise economists favor revenue enhancement cuts or oppose them?
One of the about fundamental divisions in American politics over the last few decades has been between those who believe that the government should cutting taxes substantially and those who disagree. Ronald Reagan rode into the presidency in 1980 partly because of his promise, shortly carried out, to enact a substantial tax cut. George Bush-league lost his bid for reelection against Bill Clinton in 1992 partly because he had broken his 1988 promise: "Read my lips! No new taxes!" In the 2000 presidential election, both George West. Bush and Al Gore advocated substantial tax cuts and Bush succeeded in pushing a package of revenue enhancement cuts through Congress early in 2001. Disputes over taxation cuts often ignite at the state and local level too.
What side are economists on? Do they back up wide tax cuts or oppose them? The answer, unsatisfying to zealots on both sides, is that it depends. One event is whether the tax cuts are accompanied by equally large regime spending cuts. Economists differ, as does any wide cross-section of the public, on how large government spending should be and what programs might be cut back. A second result, more relevant to the give-and-take in this affiliate, concerns how close the economy is to the total employment level of output. In a recession, when the intersection of the Advertizement and As curves is far below the full employment level, revenue enhancement cuts can make sense as a way of shifting Advert to the right. Nonetheless, when the economy is already doing extremely well, tax cuts may shift AD so far to the right every bit to generate inflationary pressures, with picayune gain to GDP.
With the AD/AS framework in mind, many economists might readily believe that the Reagan tax cuts of 1981, which took effect just later on ii serious recessions, were beneficial economic policy. Similarly, the Bush tax cuts of 2001 and the Obama taxation cuts of 2009 were enacted during recessions. Nonetheless, some of the same economists who favor tax cuts in time of recession would be much more dubious almost identical tax cuts at a time the economy is performing well and cyclical unemployment is depression.
The use of government spending and tax cuts can exist a useful tool to affect aggregate demand and information technology will be discussed in greater detail in the Government Budgets and Fiscal Policy chapter and The Impacts of Authorities Borrowing. Other policy tools tin shift the amass demand curve as well. For example, equally discussed in the Monetary Policy and Bank Regulation chapter, the Federal Reserve can impact interest rates and the availability of credit. College involvement rates tend to discourage borrowing and thus reduce both household spending on large-ticket items like houses and cars and investment spending by business. Conversely, lower involvement rates will stimulate consumption and investment demand. Interest rates can besides affect exchange rates, which in turn will take effects on the export and import components of aggregate demand.
Spelling out the details of these alternative policies and how they affect the components of aggregate demand tin wait for The Keynesian Perspective chapter. Here, the central lesson is that a shift of the amass demand curve to the right leads to a greater real Gdp and to upwards pressure on the cost level. Conversely, a shift of aggregate demand to the left leads to a lower real Gdp and a lower price level. Whether these changes in output and cost level are relatively big or relatively modest, and how the alter in equilibrium relates to potential Gross domestic product, depends on whether the shift in the Advert curve is happening in the relatively flat or relatively steep portion of the AS bend.
Key Concepts and Summary
The AD curve volition shift out every bit the components of aggregate demand—C, I, G, and 10–M—rise. It will shift back to the left as these components fall. These factors tin change because of different personal choices, similar those resulting from consumer or business confidence, or from policy choices like changes in government spending and taxes. If the Advertisement curve shifts to the right, then the equilibrium quantity of output and the price level volition ascension. If the Advertising curve shifts to the left, and so the equilibrium quantity of output and the price level will fall. Whether equilibrium output changes relatively more than than the price level or whether the price level changes relatively more output is determined by where the AD curve intersects with the Equally curve.
The AD/Every bit diagram superficially resembles the microeconomic supply and demand diagram on the surface, just in reality, what is on the horizontal and vertical axes and the underlying economical reasons for the shapes of the curves are very unlike. Long-term economic growth is illustrated in the Advertisement/AS framework by a gradual shift of the aggregate supply curve to the right. A recession is illustrated when the intersection of Ad and Equally is substantially beneath potential GDP, while an expanding economic system is illustrated when the intersection of As and AD is near potential Gdp.
Self-Check Questions
- How would a dramatic increase in the value of the stock market shift the AD bend? What effect would the shift take on the equilibrium level of Gross domestic product and the price level?
- Suppose Mexico, i of our largest trading partners and purchaser of a large quantity of our exports, goes into a recession. Employ the AD/AS model to decide the likely bear upon on our equilibrium Gdp and price level.
- A policymaker claims that tax cuts led the economy out of a recession. Can we apply the Advertisement/AS diagram to show this?
- Many financial analysts and economists eagerly await the press releases for the reports on the abode cost index and consumer conviction index. What would be the effects of a negative report on both of these? What about a positive report?
Review Questions
- Name some factors that could crusade AD to shift, and say whether they would shift AD to the right or to the left.
- Would a shift of Ad to the right tend to make the equilibrium quantity and price level college or lower? What near a shift of AD to the left?
Critical Thinking Questions
- If households decide to relieve a larger portion of their income, what outcome would this accept on the output, employment, and toll level in the short run? What about the long run?
- If firms get more optimistic about the futurity of the economy and, at the same time, innovation in 3-D printing makes most workers more productive, what is the combined upshot on output, employment, and the cost-level?
- If Congress cuts taxes at the same time that businesses become more pessimistic nearly the economic system, what is the combined effect on output, the price level, and employment using the AD/Equally diagram?
Solutions
Answers to Self-Cheque Questions
- An increment in the value of the stock market would brand individuals feel wealthier and thus more than confident well-nigh their economical situation. This would probable crusade an increase in consumer confidence leading to an increase in consumer spending, shifting the AD curve to the right. The result would be an increase in the equilibrium level of Gross domestic product and an increase in the toll level.
- Since imports depend on GDP, if Mexico goes into recession, its Gross domestic product declines and so do its imports. This reject in our exports tin can exist shown equally a leftward shift in AD, leading to a decrease in our GDP and price level.
- Taxation cuts increment consumer and investment spending, depending on where the tax cuts are targeted. This would shift Advert to the right, and so if the tax cuts occurred when the economic system was in recession (and GDP was less than potential), the tax cuts would increment GDP and "lead the economy out of recession."
- A negative report on home prices would brand consumers experience like the value of their homes, which for most Americans is a major portion of their wealth, has declined. A negative written report on consumer conviction would make consumers experience pessimistic virtually the future. Both of these would probable reduce consumer spending, shifting AD to the left, reducing GDP and the cost level. A positive report on the dwelling house price index or consumer conviction would exercise the reverse.
Source: https://opentextbc.ca/principlesofeconomics/chapter/24-4-shifts-in-aggregate-demand/
Posted by: riddlethiste.blogspot.com

0 Response to "Which Of The Following Will Most Likely Occur In An Economy If More Money Is Demanded"
Post a Comment